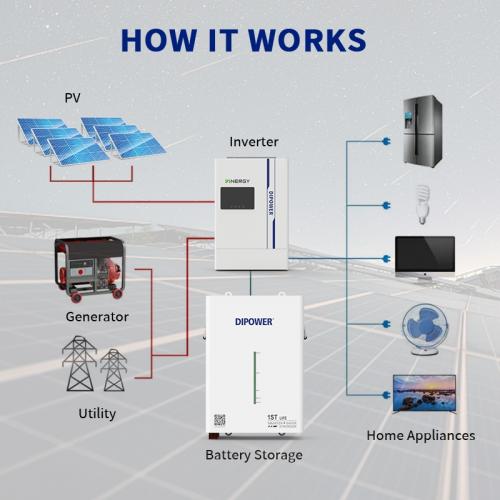
What does LiFePO4 stand for?

LiFePO4 stands for lithium iron phosphate, a type of lithium-ion battery technology. In recent years, LiFePO4 batteries have gained popularity due to their superior safety, longevity, and environmental benefits compared to other lithium-ion chemistries. Understanding the intricacies of LiFePO4 batteries can be beneficial for both consumers and industries looking to leverage renewable energy sources and efficient energy storage solutions.
LiFePO4 batteries are known for their robustness and stability. Unlike other lithium-ion batteries, which use cobalt oxide or manganese oxide, LiFePO4 uses iron phosphate as the cathode material. This difference in chemistry provides several advantages. Firstly, LiFePO4 batteries are less prone to thermal runaway, a condition that can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. This makes them inherently safer, particularly in applications where safety is a critical concern, such as in electric vehicles, medical devices, and energy storage systems.
Another notable advantage of LiFePO4 batteries is their longevity. These batteries can endure a higher number of charge and discharge cycles compared to their counterparts. Typically, a LiFePO4 battery can last for more than 2,000 cycles, whereas other lithium-ion batteries might only last between 500 to 1,000 cycles. This extended lifespan makes them an economical choice in the long run, despite a potentially higher upfront cost.
Environmental impact is another area where LiFePO4 batteries excel. The use of iron phosphate reduces the reliance on cobalt, a material that is not only expensive but also associated with significant ethical and environmental concerns. Cobalt mining has been linked to human rights abuses and environmental degradation, making the shift towards cobalt-free technologies like LiFePO4 a more sustainable choice.
From a performance standpoint, LiFePO4 batteries offer a stable output voltage, which can be crucial for applications requiring a consistent power supply. They also have a lower self-discharge rate, meaning they retain their charge for longer periods when not in use. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for backup power systems and off-grid energy solutions.
However, like any technology, LiFePO4 batteries are not without their limitations. One of the primary drawbacks is their energy density, which is lower than other lithium-ion batteries. This means that for the same capacity, a LiFePO4 battery will generally be larger and heavier. While this might be a disadvantage in applications where space and weight are premium, such as in portable electronics, it is less of a concern in stationary applications like home energy storage systems.
The cost is another factor to consider. Although the price of LiFePO4 batteries has been decreasing, they are still relatively more expensive than other lithium-ion options. However, when factoring in their extended lifespan and safety benefits, the total cost of ownership can be competitive.
In practical applications, LiFePO4 batteries are making significant inroads. In the automotive industry, they are being used in electric vehicles (EVs) due to their safety and longevity. Major EV manufacturers are increasingly adopting LiFePO4 technology, recognizing its potential to improve vehicle safety and reduce costs associated with battery replacement.
In the realm of renewable energy, LiFePO4 batteries are being integrated into solar power systems. Their ability to efficiently store and discharge energy makes them ideal for solar applications, where energy storage is crucial for balancing supply and demand. Homeowners and businesses are turning to LiFePO4 batteries to enhance their solar installations, ensuring a reliable power supply even when the sun isn’t shining.
Moreover, LiFePO4 batteries are finding applications in grid energy storage. As the world transitions to more renewable energy sources, the need for efficient and reliable energy storage solutions is becoming increasingly important. LiFePO4 technology offers a viable solution, providing the stability and longevity required for large-scale energy storage.
In conclusion, LiFePO4 stands for lithium iron phosphate, a battery technology that offers significant advantages in terms of safety, longevity, and environmental impact. While there are some limitations, such as energy density and cost, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks in many applications. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see even greater adoption of LiFePO4 batteries across various industries, driving innovation and contributing to a more sustainable future. Whether you are a consumer looking for a reliable battery solution or an industry professional exploring energy storage options, understanding the potential of LiFePO4 technology is crucial in making informed decisions.